What is a Data Structure?
- Feb 15, 2023
- 2 min read
A data structure is a type of storage method for organizing and storing data. It is a method of organizing data on a computer so that it can be easily accessed, modified and updated. It is also used in the processing, retrieving, addition and deletion of data.
Today, every software and programs that we are using consists of different basic and advanced types of data structures. Hence it is important to understand the basics of data structures in order to design efficient algorithms and write efficient and scalable software.
Why Do We Need Data Structure ?
Take a library, for instance, where many books are available. They could use a data structure like a binary search tree to store the books based on their titles, authors, or ISBN numbers if they wanted to handle the books effectively. Their ability to swiftly add or remove books from the collection as well as quickly search for a certain book based on its characteristics is made possible by this method.
An e-commerce website is another real-world example where a lot of customer and product data is stored. They could store and retrieve this data effectively using data structures like arrays, linked lists, and hash tables, facilitating speedy information search and retrieval.
Now before starting with basics of data structures let’s clarify some doubts regarding data structures.
Is Data Structure a programming language ?
No, Data Structure is not a programming language like Java, C or C++.
Basically these are a set of Algorithms which gives the basic logic to execute a program or a software and structure data in a memory and these algorithms are implemented in different programming languages.
Classification of Data Structures :
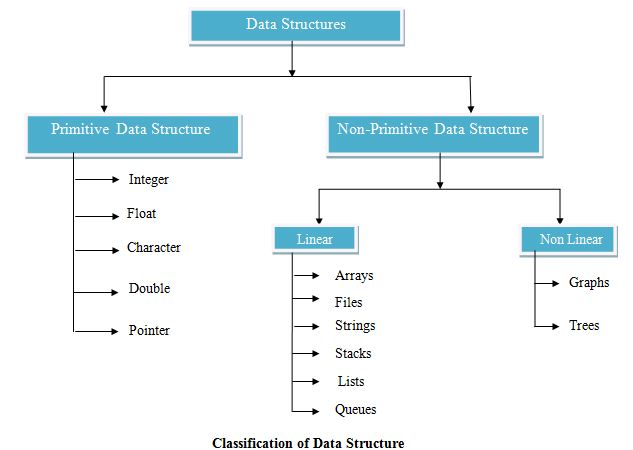
Primitive Data structures:
These are basic or predefined data structures that can be used to build more complex data structures. They are supported by all programming languages.
Primitive data structures include integers, floating-point numbers, real numbers, characters etc. Primitive Data Structures are the building blocks for non-primitive data structures which allows for more complex organization and manipulation of data.
Non-Primitive Data Structures:
These data structures are not predefined in any programming language. They are built with the help of primitive data structures.
Examples include arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs etc.
Non-Primitive data structures are further classified as linear and non-linear -
Linear Data Structure - These Data Structures store data in a linear or sequential fashion where elements are stored one after another. Examples include Arrays, Linked List, Stack etc.
Non Linear Data Structure - These Data Structures store data in a non-linear or random fashion where elements are stored and connected to each other but in a complex manner unlike linear data structures. Examples include Trees and Graphs.




Comments