Top 5 Classic Linked List Interview Questions with Java Solutions and Explanations
- Mar 26, 2023
- 4 min read
Updated: Mar 28, 2023

In the previous articles we learnt about Linked Lists from basic to advance. Now it’s time to implement the concepts of Linked Lists to solve some classic questions asked in most interview rounds.
Here are my selections for the top 5 questions based on their popularity and effectiveness in assessing knowledge of linked lists in Java:
How do you reverse a linked list?
How do you find the middle element of a linked list?
How do you detect if a linked list has a loop/cycle?
How do you merge two sorted linked lists into one sorted linked list?
How do you remove duplicates from a sorted linked list?
The scope of significant linked list operations covered by these questions includes traversal, modification, and merging. Correctly answering these questions necessitates a thorough knowledge of linked lists and Java's implementation of them.
Now we are going to start with our questions.
Question 1: How do you reverse a linked list?
Approach -
By altering each node's pointer, the linked list can be reversed. The current node, previous node, and next node are three pointers that we can keep track of. The current node's next pointer can then be changed to point to the preceding node. The next step is to shift the current node to the next node and the current node
Code -

Explanation -
prev and curr are the first two pointers we use in this code. prev was initially set to null, while curr was initially set to the linked list's head. The linked list is then iterated over in a loop until curr is null.
The next node of curr is kept track of inside the loop by being kept in a temporary variable called nextTemp. Then, we modify curr's next pointer such that it now points to previous. Next, we switch from prev to curr and from curr to nextTemp.
prev, which now points to the new head of the reversed linked list, is returned at the end.
Question 2: How do you find the middle element of a linked list?
Approach -
The middle element of the linked list can be located by using two pointers. Whereas the second pointer moves two nodes at once, the first pointer only moves one node at a time. The first pointer will be referring to the middle node by the time the second pointer reaches the end of the linked list.
Code -

Explanation -
We begin with two pointers in this code: slow and fast. Both of the pointers originally point to the linked list's head. The linked list is then iterated through until fast reaches its conclusion.
We go quickly two nodes at a time and slowly through the loop. slow will be pointing to the middle node when quick reaches the end of the linked list.
Last but not least, we return slow, which points to the linked list's middle node.
Question 3: How do you detect if a linked list has a loop/cycle?
Approach -
To determine if a linked list has a loop or cycle, we can utilise two pointers. Whereas the second pointer moves two nodes at once, the first pointer only moves one node at a time. The second pointer will eventually overtake the first pointer if the linked list contains a loop.
Code -
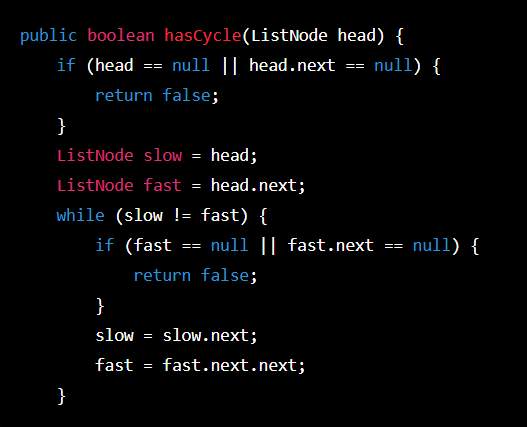
Explanation -
We begin with two pointers in this code: slow and fast. fast initially points to the second node of the linked list, while slow initially points to the linked list's head.
After slow and fast are equal, we loop through the linked list once more. Then, we determine whether the loop is fast or fast.next. Since there is no loop in the linked list, next is null.
If fast and fast.next are not null, we travel quickly through two nodes at once and slowly through one node at a time. If the linked list contains a loop, fast will eventually overtake slow, and the two will be equal.
Lastly, we return true, indicating that the linked list has a loop, if slow and fast are equal.
Question 4: How do you merge two sorted linked lists into one sorted linked list?
Approach -
To combine two sorted linked lists into one sorted linked list, we can employ a recursive method. We begin by contrasting the values of the two linked lists' initial nodes. The top of the merged list is whichever node with the smallest value. Then, using the other linked list and the node of the list with the smaller value, we recursively call the function.
Code -

Explanation -
With this code, the first thing we do is see if either l1 or l2 are null. We return the other linked list if one of them is nil.
We compare the values of l1 and l2 only if neither is null. The head of the merged list is whichever of the connected lists has the smaller value. On the next node of the list with the smaller value and the second linked list, we then run the mergeTwoLists function.
This procedure is repeated until one of the connected lists is null. The remaining nodes from the other linked list are now included in the merged list.
Lastly, we provide you with the merged list's head.
Question 5: How do you remove duplicates from a sorted linked list?
Approach -
Since the linked list is already sorted, we only need to iterate through it and compare each node's value to the value of the node after it. We eliminate the following nodes if they are equal.
Code -

Explanation -
This code initially determines whether the linked list is empty or has just one node. If so, we give you the linked list's head back.
If there are multiple nodes in the linked list, we begin iterating through the list from the head. We compare each node's value with that of its neighboring node. If they are the same, we remove the following node by modifying the current node's next pointer to remove the following node. If not, the linked list's next node is reached.
This procedure is repeated until the linked list's conclusion. Lastly, we give you the changed linked list's head.
The numerous linked list operations and algorithms must be understood in order to effectively tackle the linked list questions that frequently appear in coding interviews. The five classic linked list interview questions, their methodologies, and Java answers were all discussed in this blog. You can boost your coding abilities, develop a better grasp of linked lists, and raise your chances of succeeding in coding interviews by comprehending these questions.




Comments